
سال اول- آبان ماه 94 - شماره دوم
به نام خدای بخشاینده ی بخشایشگر
همکاران عزیز ویاران همراه!
سلام
حال که با عنایت خداوند منان نگارش وگرداوری خبرنامه انجمن استرابیسم ونوروافتالمولوژی شروع شده و گردش منظم خود را طی می کند;مساعدت وهمکاری شما عزیزان راهم می طلبد.باشد که ما رادرپیشرفت این مجموعه یاری فرمایید.
AAPOS Workshop
Surgical management of strabismus in Duane retraction syndrome
Ramesh Kekunnaya, MD, FRCS,aStephen Kraft, MD, FRCSC,bVenkateshwar B. Rao, MD,c Federico G. Velez, MD,d,e,fVirenderSachdeva, MS,gand David G. Hunter, MD, Phd
J AAPOS 2015;19:63-69
در حالیکه DRS نسبتا شایع است ;ولی به خاطر چهره های گوناگون کلینیکی وشدت گوناگون فقدان Abduction&Adduction جراحی های ان چالش برانگیز است.در این گارگاه جراحان مجرب در مورد جراحی های استرابیسم در این سندرم به بحث می نشینند.
اگرچه بیشتر کلینیسین ها از تقسیم بندی Huber در انواع دوئن پیروی میکنند(تقسیم بندی بر اساس میزان ابداکشن واداکشن ); به نظر میرسدتقسیم بندی بر اساس esotropic, exotropic, orthotropicدر پلن گذاری و درمان مفید تر باشد.
1)-Unilateral, Esotropic DRS
نوع جراحی موارد دوئن ET یکطرفه بستگی به موارد زیر دارد:
1- شدت انحراف در پوزیشن اولیه
2- میزان محدودیت در ابداکشن
3- شدت رترکشن در اداکشن
4- شدت upshoot/downshoot در اداکشن
5- وسعت میدان دید دو چشمی
Unilateral medial rectus recession
این درمان موثری برای انحراف∆20≥ میباشد.البته میزان رسس به عقیده برخی نباید بیش از mm 6وبه عقیده برخی دیگر mm 5 باشد.علت این محدودیت ایجاد محدودیت در adduction به صورت ایاتروژنیک وایجادexothropia در gaze مخالف می باشد. درواقع اگربهبودی در ابداکشن به خرج کاهش قابل ملاحظه میزانadductionباشد ˛اگزوتروپی در اداکشن ایجاد شود; فیلد دید دو چشمی بیمار کاهش می یابد ودیپلوپی ناتوان کننده ایجاد می شود.
مورد بعدی large recessionدرعضله مدیال سمت مقابل است. این درمان در مواردی که بیمار ابداکشن خوبی (2- وبهتر ) دارد;مفیدتر است.این روش باmatch کردن کاهش ابدوکشن در چشم DRS;فیلد دو چشمی را افزایش میدهد.
Bilatral Medial Rectus Recession
در سه حالت این درمان مفید است.
1) large angle esotropia:∆ 20≤
2) رترکشن شدید گلوب:در این موارد باید رسس عضله LR را هم انجام داد که این باعث افزایش زاویه انحراف میشود.در این صورت انجام رسس عضله مدیال سمت مقابل باید مد نظر قرار بگیرد.
3)contracture عضله MR :رسس عضله مدیال مقابل یک Fixation duressدر ان چشم ایجاد میکند.در واقع هنگام فیکساسیون با چشم غیر دوئنی باید افزایشinnervation به مدیال همان طرف وکاهش innervation به عضله لترال همان چشم وهمزمان کاهش innervationبه عضله مدیال طرف مقابل(چشم دوئن) اتفاق بیافتد.وعقیده بر اینست که این مانع contracture میشود.
میزان رسس در عضله مدیال در دو سناریو اول به اندازه باقیمانده انحراف بعد از تصحیح در چشم دوئن وحداکثر 5-6 میلیمتر می باشد .ولی در سناریو سوم رسس باید بیش از مقدار معمول 7-8 میلیمتر باشد تاایجادfixation duress نماید.
Unilateral recess&resect
شرایط لازم برای این عمل:1- میزان انحراف در primary gaze حداقل ∆25
2-رترکشن خفیف گلوب (تنگ شدن فیشر پلکی از پوزیشن اولیه به اداکشن کمتر از 33%)
3-از نظر کلینیکی اداکشن نرمال
4-محدودیت قابل توجه در ابداکشن حداقل 3.5-
6- فقدان فنومن shoot(up shoot ,down shoo) یا میزان بسیا کم ان
در گذشته جراحان از رزکشن به دلیل ایجادمحدودیت ابداکشن وبدترشدن رترکشن گلوب دوری می کردند. این هنگامی رخ میدهد که رزکشن در اندازه های 5تا 8 میلیمتر انجام شود(انچه دراسترابیسم های comitant انجام میشود).در حالیکه در موارد انتخابی دوئن رزکشن عضله لترال3تا3.5 میلیمترورسس عضله مدیال کمتر از5میلیمتربدون ایجاد عارضه قابل انجام است.
Kraft SP. Resecting the lateral rectus in unilateral Duane syndromewith esotropia and limited abduction. Binoc Vis Strab Q 2010;25: 146-57
Unilateral ExotropicDRS(2
در انحراف کمتر از20 پریسم رسس عضله لترال همان چشم ودر انحراف بیش از 20 پریسم رسس هر دو لترال انجام می شود.نویسندگان معتقدند که دوز جراحی در این موارددر مقایسه باجداول استاندارد باید افزایش یابد.
رسس عضله لترال ممکن است محدودیت ابداکشن را مخصوصا اگر از قبل وجود داشته باشد بدتر کند.بنابر این زمانی که دوطرفه رسس لترال مد نظر است باید اسیمتریک انجام شود ورسس بیشتر در سمت مقابل انجام شود.(مگرcontractureعضله لترال رکتوس همان طرف شدید باشد.)
درهمراهی overshoots با DRS-XTاضافه کردن Y-splittingبه رسس عضله لترال لازم است.
در همراهی با رترکشن متوسط تا شدید گلوب ;رسس لترال به تنهایی مفید نخواهد بود.در این حالت˛ موارد زیر قابل انجام است. 1-رسس متفاوت عضلات لترال ومدیال;2- رسس سوپرا ماکزیمال عضله لترال 3-periosteal fixation عضله لترال (به تنهایی یا با همراهی vertical rectus transposition)
Bilateral DRS(3
15% موارد دوئن را تشکیل می دهد.و بیشتر در مردان است.میزان انحراف در پوزیشن اولیه از 14 تا 70 پریسم متغیر است.در جراحی دو طرفه ریسک کاهش حرکات افقی چشم مخصوصا اگر co-contraction باشد;وجود دارد.
Globe Retraction and Overshoots(4
رسس عضله مدیال به اندازه 5تا6.5 میلیمتروعضله لترال 7تا 9 میلیمتر نیاز است.هرگاه ایزوتروپی وجود دارد باید عضله مدیال بیش از لترال رسس شود و در صورت عدم وجود انحراف باید عضله لترال یک میلیمتر بیشتر از مدیال رسس شود.برخی جراحان عقیده دارند که در بیماران adult باید دوز رسس به منظور کاهش رترکشن افزایش یابد.چون در بسیاری از بالغین ˛بافت نرم وچربی اوربیت در اثردهه ها رترکشن قالب گرفته وحتی رسس زیاد عضلات افقی تاثیر کمی بر روی آن دارد.وبعد از طی زمان وادامه co-contraction
رترکشن عود میکند.
در باره overshootsعقیده بر اینست که عضله لترال سفت بر روی گلوب به بالا یا پایین میلغزد.(bridle or leash phenomenon) .عصب گیری نابجا(dysinnervation) در عضلات عمودی هم ممکن است در این پدیده نقش داشته باشد.
در مان های رایج شامل:1-رسس عضله لترال ومدیال 2-سوچور posterior fixation روی عضله لترال چشم متاثر به تنهایی یا هم عضله لترال وهم عضله مدیال 3-رسس عضلات ورتیکال
Myectomy-4 عضله مایل تحتانی برای upshoot 5- Y-spliting با یا بدون رسس عضله لترال.
عقیده بر اینست که هر نیمه عضله دوشاخه شده پوزیشن چشم را دراداکشن بالانس میکند وقتی که چشم به بالای خط وسط در اداکشن نگاه میکند بازوی بالایی روی گلوب وبازوی پایینی زیر تنشن است.که منقبض شده ومانع لغزیدن چشم به بالا می شود.همین طور وقتی چشم به زیر خط وسط در اداکشن نگاه می کند.بازوی بالایی منقبض شده ومانع لغزیدن به پایین می شود.در واقع هر نیمه عضله پوزیشن گلوب را
در اداکشن بالانس میکند.
Reoperations Following Vertical RectusMuscle Transposition(5
Residual ET:
علت یا فقدان نیروی ابداکتوری عضلات ترانسپوز شده است یاتونوس زیاد یا انقباض عضله مدیال می باشد.که بیشترین عامل همین مورد دوم است.ریسک فاکنور دیگر زاویه انحراف زیاد در پوزیشن اولیه است.
دو عامل در عمل مجدد این بیماران مهم است.1-توانایی صاف نگه داشتن سر وقتی با چشم دوئنی فیکس می کند.که اگر در این هنگام پوزیشن غیرطبیعی سر ایجاد شود باید جراحی انجام شود.2-FDT حین عمل، اگر FDT مثبت شود رسس عضله مدیال لازم است
اگرFDT منفی باشد عضلات ترانسپوز شده قبلی باید explore شوند .(مهاجرت محل insertionیا bellyعضله به سمت منشا یا رسس عضله یا slippage یا کشیده شدن به سمت تمپورال توسط augmented suture)
Exotropia:
به دنبال VRTبه علت تنشن زیاد یا Restriction ناشی از ترانسپوزیشن ˛یا مدیال رکتوس ضعیف ˛یا تقویت co-contracture در عضله لترال یا سفت شدن آن ایجاد می شود.
عارضه XT بعد از عمل ˛باعث دوبینی و معکوس شدن تورتیکولی واغلب کم شدن میدان دید دو چشمی میشود.
ریسک فاکتورهایXTبعد از عمل
1-وجود XT در اداکشن یا کمتر شدن ETدر اداکشن در قبل از عمل است.(یعنی بیمار قبل از عمل co-contracture دارد که با عمل رسس مدیال بدتر شده است)
2-وجود جزﺀتطابقی تشخیص داده نشده
3-عضله مدیال slipped
4-stretched scar
Early overcorrection به دلیل رسس زیاد عضله مدیال وبقیه موارد فوق باعث late overcorrection می شود.ولی tight vertical rectus transposition باعث هم XT زودرس وهم دیررس می شود. در درمان overcorrectionا˛FDTکمک کننده است .اگر FDTمنفی باشدبایدadvancement عضله مدیال همان طرف انجام شود.واگر مثبت باشدیا علت در VRTاست˛ یا عضله لترال رکتوسtightاست.
علت tightشدن لترال
1-کوتاه شدن پاسیو فیبر ها درپوزیشن XT
2-تشدید co-contracture در اثر رسس عضله مدیال
3- ایجاد بافت اسکار از VRT . در این صورت با گذاشتن هوک زیر عضله لترال وانجام FDTمجدد میتوان به میزان stiffnessعضله لترال پی برد.
هنگامی که FDT مثبت باشد;درمان˛reposition عضلات ترانسپوز شده با یا بدون رسس عضله لترال همان طرف است.جراح ابتدا باید augmented suture را آزاد کرده هر نوع اسکاری را بین عضله واسکلرا بردارد وسپس مجدد FDT کرده ودر صورت مثبت بودن ˛عضلات را در همان مسیر ترانسپوزیشن رسس کند.
Induced vertical deviation
مکانیسم ایجاد آن:1-رسس غیر منتظره یا slippage یکی از عضلات ترانسپوز شده
2-ضعف عضله ورتیکال در اثر از دست دادن نیروی ورتیکال
برای درمان بایدaugmented suture را برداشت ورسس عضله ورتیکال 1.5 تا 3 میلیمترانجام داد وسپس augmented suture را طوری که محدودیتی ایجاد نکند ˛تعبیه کرد.
اگر FDT منفی بود˛exploration عضلات ترانسپوز شده و برگرداندن نسبی انها لازم است.از طرفی جدا سازی اتصالات عضله رکتوس تحتانی از فاشیای کپسولو پالپبرال ولیگامان لاکوود مانع ایجاد این عارضه می شود.وهمچنین جداسازی اتصالات میان عضله رکتوس فوقانی و فرنولوم ومایل فوقانی مانع ایجاد تورشن ثانویه وعوارض ورتیکال میشود.(بافت اسکار بین تاندون عضله مایل فوقانی واینسرشن عضله رکتوس فوقانی مسیر تاندون را عوض میکند وان را بهanti depressor مکانیکال تبدیل میکند.)
راه دیگر حذف انحراف ورتیکال جدید ˛حذف جابجایی عضله رکتوس تحتانی است.(SRT)
Role of Superior Rectus Transposition
Jonson وهمکارانشدر 2006تکنیک جدیدی را فقط با ترانسپوز کردن تنها رکتوس فوقانی معرفی کردندونتایج خوبی از این مطالعه گزارش کردند.
An innovative approachto transposition surgery is effective in treatment of Duane’syndrome withesotropia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:ARVO E-Abstract 2475
در مطالعه دیگری Mehendale وهمکارانش SRT رابا رسس عضله مدیال به صورتAdjustable در 10 بیمار ET-DRS انجام دادند.در این مطالعه دیدند کهSRTبا یا بدون رسس عضله مدیال باعث بهبود انحراف و ابداکشن میشود.
Superior Rectus Transposition and Medial Rectus Recession for Duane Syndrome
and Sixth Nerve Palsy
Reshma A. Mehendale, MD; Linda R. Dagi, MD; Carolyn Wu, MD; Danielle Ledoux, MD; Suzanne Johnston, MD; David G. Hunter, MD, PhD
Objective:To describe our results using augmented temporalsuperior rectustransposition (SRT) with adjustablemedial rectus muscle recession (MRc) for treatmentof Duane syndrome and sixth nerve palsy.
Methods: Retrospective surgical case review of patientsundergoing SRT. Preoperative and postoperativeorthoptic measurements were recorded. Minimum follow-up was 6 weeks. Main outcome measures includedthe angle of esotropia in the primary position and the angleof head turn. Secondary outcomes included duction limitation,stereopsis, and new vertical deviations.
Results: The review identified 17 patients: 10 withDuane syndrome and 7 with sixth nerve palsy. CombiningSRT with MRc improved esotropia from 44 to 10 prism diopters (P=.001), reduced abduction limitationfrom −4.3 to −2.7 (P=.001), and improved compensatoryhead posture from 28° to 4° (P=.001). Stereopsis was recovered in 8 patients (P=.03). Three patients requireda reoperation: 1 for overcorrection and 2 for undercorrection.A new primary position vertical deviationwas observed in 2 patients with complex sixthnerve palsy and none with Duane syndrome. No patientdescribed torsional diplopia.
Conclusions:Superior rectus transposition allows forthe option of simultaneous MRc in patients with severeabduction imitation who require transposition surgery. Combining SRT and MRc improved esotropia, head position,abduction limitation, and stereopsis without inducingtorsional diplopia.
Arch Ophthalmol. 2012;130(2):195-201
Diagram representation of the superior rectus transposition (SRT) plus medial rectus recession (MRc) procedure. A, The MRc procedure with adjustablesutures. B, The SRT technique with augmentation suture. The amount of muscle included in the augmentation suture appears in the rendering to be less than.one-quarter of the muscle width after tying the knot
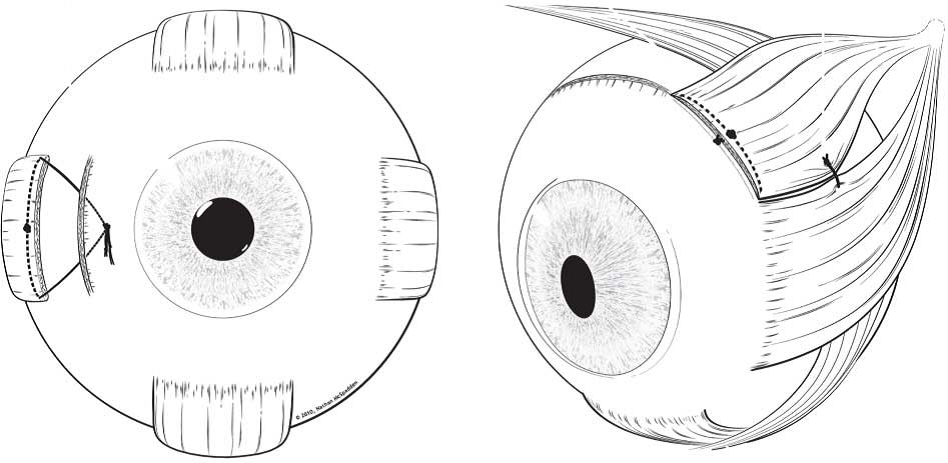
اخیرا در گزارش دیگری رسس عضله مدیال(یکطرفه یا دو طرفه)را باSTR (با یا بدون رسس مدیال رکتوس) مقایسه کردند ودیدند که اگرچه در هر دو گروه میزان انحراف و چرخش سر بهبود یافته میزان رسس عضله مدیال در گروه SRTکمتر بود وبهبود ابداکشن بهتر ونتایج طولانی مدت بهتر در گروه SRT مشاهده شد.
Superior Rectus Transposition vs Medial Rectus Recessionfor Treatment of Esotropic Duane Syndrome
Shiqiang Yang, MD; Sarah MacKinnon, MSc, OC(C); Linda R. Dagi, MD; David G. Hunter,MD, PhD
IMPORTANCE Superior rectus transposition (SRT) with or without medial rectus recession (MRc) has been introduced as an alternative toMRc alone for treatment of esotropic Duane syndrome; however, the effectiveness of these procedures has not been compared previously.
OBJECTIVE To compare the safety and efficacy ofMRc and SRT in treatment of Duane syndrome.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS Retrospective medical record review of all patients with esotropic Duane syndrome who underwent surgical treatment from January 1, 2006, through December 31, 2012, in a multispecialty, hospital-based pediatric ophthalmology/adult strabismus practice at Boston Children’s Hospital. Patients in the SRT group underwent SRT with or without MRc; those in the non-SRT group underwent unilateral or bilateral MRc.
EXPOSURES Surgical treatment of esotropic Duane syndrome.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES Binocular alignment, ocular ductions, head position, stereopsis, and fundus torsion were recorded before surgery and at the 2-month and final postoperative visits.We also evaluated postoperative drift.
RESULTS The medical record review identified 36 patients who underwent 37 procedures, including 19 in the SRT group (13 SRT + MRc and 6 SRT alone) and 18 in the non-SRT group (11 unilateral MRc and 7 bilateral medial rectus resession). Mean MRc was smaller when performed with SRT (3.3 vs 5.3 mm; P = .004). Although the initial deviation was larger in the SRT group, both groups had a similar improvement in esotropia and head turn. Abduction improved by at least 1 unit in 15 of 19 patients in the SRT group (79%) vs 5 of 18 in the non-SRT group (28%). In 24 patients followed up for more than 6 months, mean esotropiadecreased from 8.2 to 6.1 prism diopters (Δ) in the SRT group (n = 12) but increased from 7.2 to 10.9Δ in the non-SRT group (n = 12).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE The combination of SRT and MRcwas more effective than MRc or bilateral medial rectus resession at improving abduction while allowing for a smaller recession to align the eyes and eliminate a compensatory head posture. Although any surgery on the vertical rectus muscles should in theory increase the risk for vertical or torsional complications, to date this theory has not been borne out in our patients. Patients treated with SRT appear to have a reduced likelihood of long-term undercorrection.We therefore recommend SRT with adjustable MRc for treatment of Duane syndrome in patients with larger amounts of esotropia.
JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(6):669-675. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.358
در مطالعه مشابهی در مورد ایجاد عارضه تورشن بررسی شدونتایج قابل قبولی در عدم ایجاد ان به دست امد.
Assessment of torsion after superior rectus
transposition with or without medial rectus recessionfor Duane syndrome and abducens nerve palsy
Federico G. Velez, MD, Erica Oltra, MD, Sherwin J. Isenberg, MD, and Stacy L. Pineles, MD
BACKGROUND: Superior rectus transposition with or without medial rectus recession has been advocatedfor the treatment of abducens nerve palsy and esotropic Duane syndrome. Early reportshave focused mainly on postoperative ocular alignment, but there is concern that superior
rectus transposition may induce torsional misalignment. The purpose of this study was toevaluate torsional outcomes after superior rectus transposition surgery using prospectivepreoperative and postoperative torsional assessments.
METHODS: Prospective measurements were performed on all patients undergoing superior rectustransposition. Preverbal infants were assessed using fundus torsion evaluating the positionof the fovea relative to the optic nerve; older children/adults underwent double Maddoxrod (DMR)assessment of torsion.
RESULTS: A total of 11 subjects met the study inclusion criteria. The etiology of strabismus was anabducens nerve palsy (n = 7) or Duane syndrome (n = 4). For the subjects evaluated byfundus torsion (n = 4), there was no significant change in torsion for 3 (75%). For thosesubjects undergoing DMR (n = 7), there was a significant change in subjective torsion(4.7± 3.8°excyclotorsion vs 0.0±5.0°excyclotorsion; P =0.004). Esotropic deviationimproved significantly for all subjects (39∆± 23∆vs 6.5∆±13∆; P =0.001) and nosignificant mean vertical deviation postoperatively, although 1 patient had a clinicallysignificant postoperative hypertropia measuring 14∆. Abduction also improved significantly(-4.2 ± 0.9 vs-2.8 ± 1, P = 0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS:In this patient series, superior rectus transposition with medial rectus recession did not haveclinically significant induction of torsional diplopia as a result of the procedure. J AAPOS2014;18:457-460
Comparison of augmented superior rectus transposition with medial rectus recession for surgical management of esotropic Duane retraction syndrome
ShailjaTibrewal, MS,aVirenderSachdeva, MS, DNB,bMohammed Hasnat Ali, MBA,c and Ramesh Kekunnaya, MD, FRCSd
BACKGROUND: Medial rectus recession (MRc) and vertical rectus transpositions are procedures used to treat esotropic Duane retraction syndrome. Recently superior rectus transposition (SRT) combined with MRc has also been shown to improve primary alignment and abduction.
The purpose of this study is to compare the results of augmented (ie, with scleral fixation)SRT with or without MRc with either unilateral or bilateral MRc for treatment of esotropic Duane syndrome.
METHODS :The medical records of patients who underwent surgery for esotropic Duane syndrome between May 2007 and February 2013 were retrospectively reviewed. Success was defined as alignment within 8∆ of orthotropia and abnormal head posture of≥5°.
RESULTS :There were 8 patients in the SRT group (6 of whom had additional ipsilateralMRc) and 13 in the MRc group (6 unilateral and 7 bilateral). In the SRT group, the mean preoperative deviation was 20∆ of esotropia; the mean postoperative deviation, 3∆. In the MRc group, the mean preoperative deviation was 24∆of esotropia; the mean postoperative deviation, 4∆. The success rate was 87% in the SRT group; 77%, in MRc group (P =0.98). Mean abduction limitation improved from -3.6 to -2.4 units in the SRT group and from -3.6 to -3.3 units in the MRc group (P = 0.003). Induced vertical deviation or subjective torsion was not seen. Three patients in each group developed adduction limitation postoperatively.
CONCLUSIONS: Although both the procedures successfully correct esotropia in Duane syndrome, SRT with or without MRc has the additional advantage of improving abduction. ( J AAPOS 2015;19:199-205)
با توجه به مطالب فوق واز انجا که در انجام عمل VRT احتمال ایجاد انحراف ورتیکال بیشتر است و از طرفی در صورت لزوم انجام رسس عضله مدیال شانس ایسکمی سگمان قدامی بیشتر میشود ;SRT میتواند گزینه جایگزین بهتری باشد.وبه نظر نویسندگان مقاله˛در بیماری با ET 12تا 14 پریسم ممکن است SRT به تنهایی کافی باشد.ولی در انحراف 15پریسم یا بیشتر SRTبه همراهی رسس عضله مدیال (adjustable)تا 5 میلیمتربراساس میزان انحراف وسفتی عضله لترال در FDT قابل انجام است.در انحرافات بالاترمیتوان SRTرا با رسس دو عضله مدیال همراه کرد.ولی همواره باید ریسک ایجاد انحراف عمودی وتورشن را در نظر داشت.
News:
1- چهاردهمین نشست تخصصی فصلی گروه استرابیسم ونوروافتالمولوژی در تاریخ پنج شنبه 1394/07/12 در محل انجمن چشم پزشکی
2- ESA 2015_37th meeting of European strabismological Association venice. Italy 1394/7/9…..1394/7/12
3- بازآموزی استرابیسم بیمارستان فارابی 1394/07/23